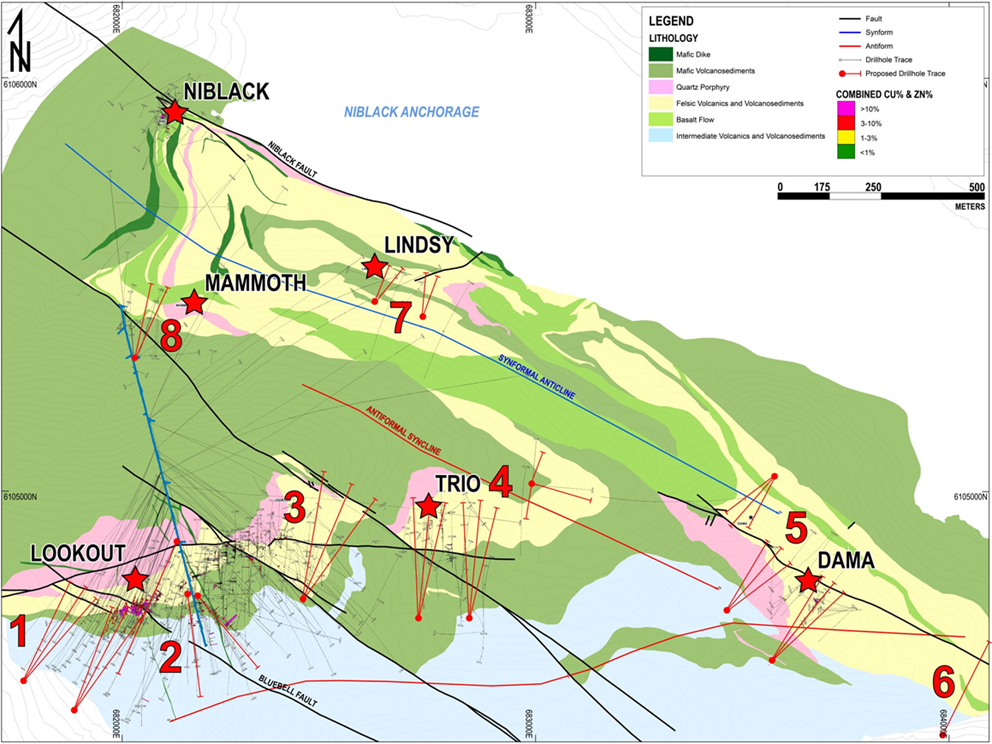
The Niblack project is a precious metal-enriched polymetallic volcanogenic massive sulphide (VMS) system hosting at least six known VMS occurrences, including the historic Niblack mine, the Dama zone, Lindsy zone, Mammoth zone as well as the Lookout and Trio deposits.
Niblack is hosted within strata of the Craig subterrane of the Neoproterozoic Alexander terrane. The Alexander terrane, which underlies the southern portion of Prince of Wales Island, formed along a convergent plate margin in the late Precambrian to Early Devonian time.
Wales Group strata at the Niblack Property consists of a bimodal sequence of mafic and felsic volcanic flows, domes, and volcaniclastics overlain by interlayered mafic volcanosedimentary wackes and pillow basalts. This package is overlain by Moira Sound Unit younger volcanosedimentary cover (see Figure 1).
Within the Wales Group sequence, a stratigraphic framework has been defined for the Niblack property which breaks the stratigraphy into three distinctive units: the Niblack Stratigraphic Footwall Succession, the Niblack Felsic Succession and the Niblack Stratigraphic Hanging Wall Succession. The Footwall Succession is consistent of dacitic to basaltic volcanics and volcaniclastics and the Hanging Wall Succession is constituted of mafic volcanosediments and basaltic pillow lavas.
Most notably, the 100-200m Niblack Felsic Succession hosts all known VMS mineralization on the property. This thick sequence of prospective folded rhyolitic volcanic rocks extends for at least six miles across the property and hosts six known massive sulphide zones: the historic Niblack mine, the Dama zone, Lindsy zone, and Mammoth zone, as well as the Lookout and Trio deposits.
The style of mineralization at Niblack is varied, but dominated by sub-seafloor replacement style semi-massive sulphide mineralization in the matrix of felsic debris flows and pyroclastics, which defines the Lookout and Trio deposits as well as the Dama zone. The historic Niblack Mine, along with the Mammoth and Lindsy zones, are characterized by seafloor exhalative pyrite-chalcopyrite-sphalerite mineralization indicating emplacement at surface and higher in the stratigraphic column than Lookout, Trio, and Niblack. Secondary classic stringer and stockwork zones are present at the Trio deposit accompanying the more prominent sub-seafloor replacement style mineralization.
The Niblack stratigraphic package has been subject to multiple phases of later deformation and greenschist facies metamorphism which occurred during the Middle Cambrian to Early Ordovician and the Middle Silurian to early Devonian. Renewed deformation occurred during the accretion of the Alexander terrane to the Cordillera in the mid-Jurassic to Cretaceous. Folding on the property is north-vergent, moderate to tight, and overturned. The six known VMS zones sit on a property-scale synformal anticline-antiformal syncline pair.
Figure 1: Plan view of the Niblack property showing geology, target areas, and propsed drill holes (red)
Exploration Potential and Reinterpretation:
Earlier operators interpreted the folds to be a simple property-scale anticlinal-synclinal pair. However, in most recent stages of exploration and research, U-Pb age dating and analysis of way-up indicators in sedimentary and volcanosedimentary beds led to the discovery that the stratigraphy is overturned. This breakthrough led to a reinterpretation of these folds as an overturned synformal anticline-antiformal syncline pair. This reinterpretation was not tested in previous exploration and opens a large new prospective area across the property based on the new projection of the permissive Niblack Felsic Succession. This reinterpreted model is driving current exploration, which is targeting and testing these newly defined prospective zones.
Recent Exploration Results:
Blackwolf has completed two exploration programs on Niblack since 2020 and are summarized below. In addition the company hold an approved Plan of Operations on the project for additional mapping, geophysical and geochemical surveys, and additional drilling from up to 15 additional sites as surface.
2020 Niblack Mine Drilling:
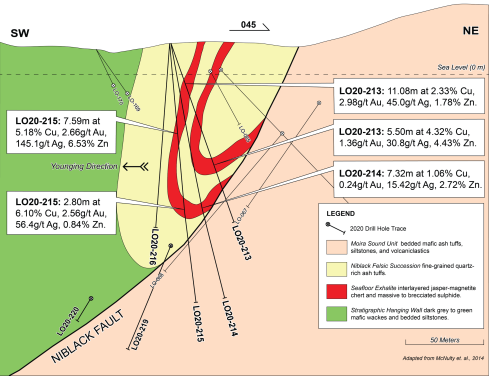
In 2020 Q4, Blackwolf completed a 10-hole, 1774-meter surface diamond drill program targeting down-dip and along-strike extension of the Niblack zone. Drilling also confirmed the newly defined and previously untested overturned fold theory. Select grades and intercepts from 2021 drilling include(1):
- LO20-213: 11.08m at 2.33% Cu, 2.98 g/t Au, 45.0 g/t Ag & 1.78% Zn
- LO20-213: 5.50m at 4.32% Cu, 1.36 g/t Au, 30.8 g/t Ag & 4.43% Zn
- LO20-215: 7.59m at 5.18% Cu, 2.66 g/t Au, 145.1 g/t Ag & 6.53% Zn
- LO20-215: 2.80 meters averaging 6.10% Cu, 2.56 g/t Au, 56.4 g/t Ag, 0.84% Zn
- LO20-219: 3.10m at 9.34% Cu, 4.25 g/t Au, 76.3 g/t Ag, 3.23% Zn
- LO20-222: 4.74 meters averaging 2.28% Cu, 0.33 g/t Au, 9.5 g/t Ag, 0.06% Zn
- LO20-224: 1.50 meters averaging 1.72% Cu, 8.02 g/t Au, 27.7 g/t Ag, 0.37% Zn
Figure 2: Vertical section (section window +/- 25m) through the Niblack Zone showing historic and 2020 drillhole traces, grade and intercept assay highlights, zone trace, and geology.
2021 Lookout Deposit Drilling
Blackwolf completed a 5-hole, 1810-meter underground diamond drill program in 2021 Q1, targeting down-dip extension and resource infill at the Lookout Zone.
Select grades and intercepts from 2021 drilling include(2):
- U21-226: 27.00m at 1.06% Cu, 1.87 g/t Au, 32.83 g/t Ag & 1.04% Zn
- Including 4.00m at 2.61% Cu, 4.93 g/t Au, 76.58 g/t Ag, 2.34% Zn
- U21-227: 32.60m at 1.03% Cu, 1.49 g/t Au, 26.54 g/t Ag, 0.92% Zn
- Including 3.00m at 2.37% Cu, 3.29 g/t Au, 58.27 g/t Ag & 1.42% Zn
(1) Refer to the Company's News Release dated May 3, 2021. Available on SEDAR.
(2) Refer to the Company's News Release dated June 16, 2021. Available on SEDAR.